The Future of Cars: How Technology, Sustainability, and Innovation Are Redefining the Road

The automotive industry is undergoing a transformation unlike any other in its history. Cars, once seen purely as machines for transportation, are rapidly evolving into intelligent, sustainable, and highly personalized mobility solutions. From electric powertrains and autonomous driving to connected infotainment systems, the future of cars is reshaping not only how we drive, but how we live, work, and interact with technology.
The Shift Toward Electric Vehicles (EVs)
One of the most significant shifts in the automotive world is the rise of electric vehicles. EVs have moved beyond niche status and are quickly becoming mainstream, thanks to advancements in battery technology, increased charging infrastructure, and global efforts to reduce carbon emissions. Companies like Tesla, Rivian, and BYD have set the pace, while legacy manufacturers such as Ford, General Motors, and Volkswagen are investing billions to electrify their lineups.
Why the surge in EV popularity? Several factors are driving adoption:
-
Environmental concerns: With climate change at the forefront of global conversations, consumers and governments alike are seeking ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Cost efficiency: Although EVs can carry a higher upfront cost, their lower maintenance requirements and reduced fuel expenses make them appealing in the long run.
-
Performance: Modern EVs offer instant torque, smooth acceleration, and increasingly impressive ranges, making them a thrill to drive.
In the coming decade, EVs are expected to dominate the roads, with more affordable models and faster-charging batteries making them accessible to a wider audience.
Autonomous Driving: From Concept to Reality
Self-driving cars, once a futuristic fantasy, are now inching closer to reality. Companies like Waymo, Cruise, and Tesla are testing autonomous systems capable of navigating complex urban environments. While fully autonomous vehicles (Level 5) are not yet available for widespread consumer use, semi-autonomous features—such as adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and self-parking—are becoming standard in many new models.
The benefits of autonomous driving could be immense:
-
Safety: Reducing accidents caused by human error, which accounts for the majority of crashes.
-
Efficiency: Smarter traffic flow and reduced congestion through connected vehicle networks.
-
Convenience: Allowing drivers to reclaim time during commutes by reading, working, or relaxing while the car handles the road.
However, challenges remain, including regulatory hurdles, technological refinement, and public trust. It may take several more years before fully self-driving cars are commonplace, but the foundation is already being built.
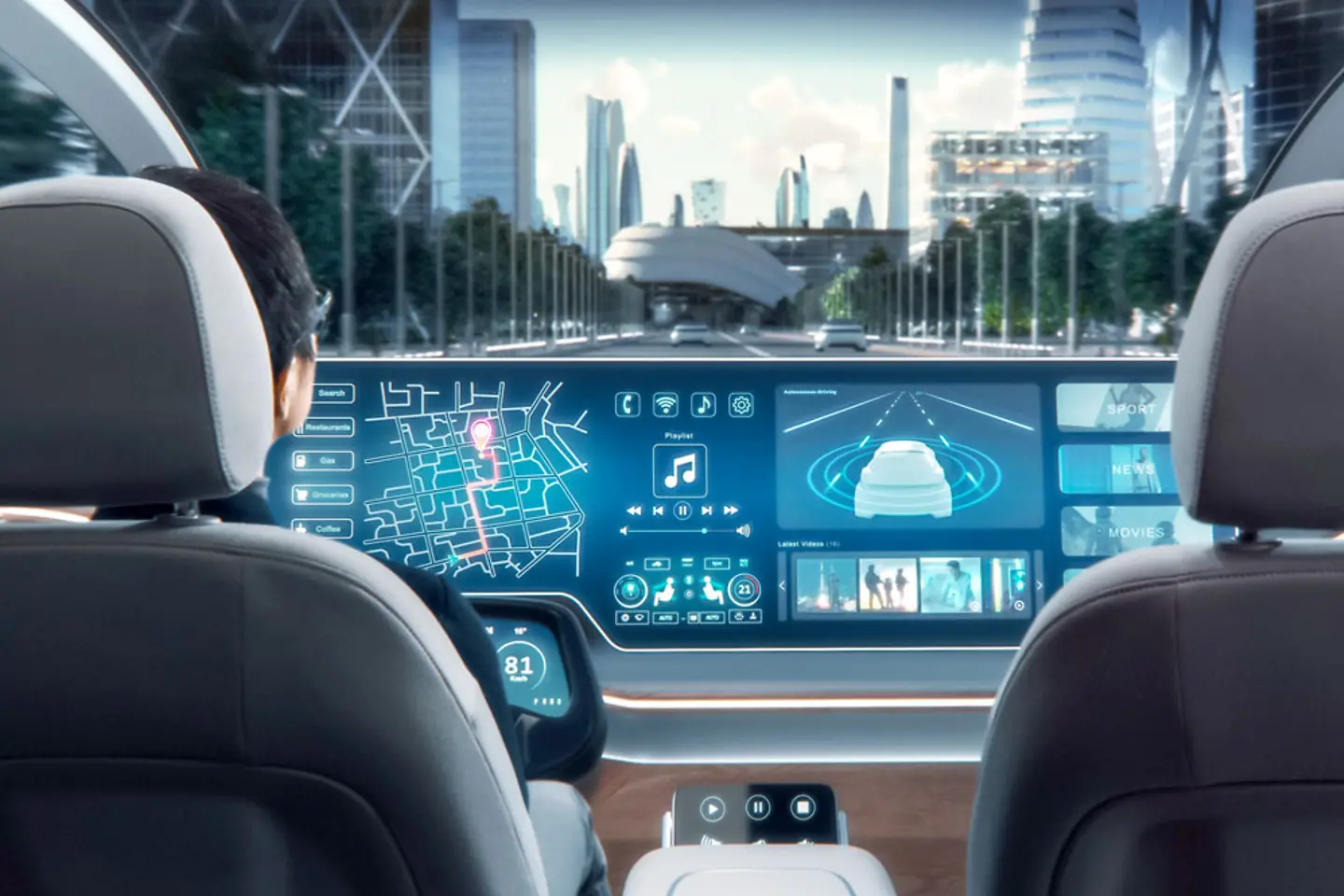
Connected Cars: Turning Vehicles Into Smart Devices
Cars are no longer isolated machines; they’re becoming extensions of our digital lives. Modern vehicles come equipped with sophisticated infotainment systems, over-the-air software updates, and seamless smartphone integration. Voice assistants, real-time navigation, and even subscription-based features—such as heated seats or performance upgrades—are becoming part of the driving experience.
5G technology is expected to revolutionize connected cars by enabling faster communication between vehicles, infrastructure, and the cloud. This could pave the way for advanced safety systems, predictive maintenance, and more personalized driving experiences. Imagine your car suggesting the fastest route home, pre-heating the cabin based on your schedule, or booking a service appointment automatically when it detects a maintenance issue.
The Rise of Sustainable Materials and Design
Sustainability isn’t just about electric drivetrains—it’s influencing the entire car-making process. Automakers are increasingly using recycled and renewable materials to reduce the environmental footprint of production. BMW, for instance, incorporates recycled plastics and plant-based materials into its interiors, while other brands experiment with lightweight composites to improve efficiency.
Car-sharing and subscription models are also growing in popularity, reducing the need for individual car ownership and cutting down on the total number of vehicles produced. These innovations reflect a broader shift toward viewing cars not just as personal property, but as services that can be tailored to individual needs.
Performance and Enthusiast Cars Still Have a Place
While the industry moves toward electric and autonomous vehicles, performance and enthusiast cars aren’t disappearing—they’re evolving. Electric sports cars like the Porsche Taycan and Rimac Nevera prove that high performance and sustainability can coexist. Additionally, hybrid systems in performance models are offering the best of both worlds: thrilling power combined with improved efficiency.
For car enthusiasts, this is an exciting era where new technologies are enhancing performance rather than replacing it. From track-focused electric hypercars to sophisticated driving-assist systems that make high-powered machines more approachable, the future still has plenty to offer those who love the thrill of the drive.
Challenges Facing the Automotive Future
Despite these innovations, the road ahead isn’t without obstacles. Supply chain issues, rising raw material costs, and the need for expanded charging infrastructure remain significant challenges. Consumer adoption also depends on affordability and convenience—particularly for EVs, where charging speed and range anxiety still concern many drivers.
Governments and automakers must collaborate to ensure that infrastructure, regulations, and innovation advance together. Without this coordination, the transition to electric and autonomous vehicles could face delays.

What the Future Holds
Looking ahead, the next decade promises to be a defining period for the automotive industry. We can expect:
-
Widespread electrification of nearly every vehicle segment, including trucks and SUVs.
-
Improved autonomous systems that bring us closer to fully self-driving vehicles.
-
Greater connectivity, making cars integral parts of smart cities and personal tech ecosystems.
-
More sustainable production practices that reduce the environmental impact of manufacturing.
For consumers, this future means more choices, smarter technology, and cleaner transportation. Cars will no longer just take us from point A to point B—they’ll be hubs of convenience, safety, and innovation, shaping how we move through the world.